NUS scientists uncover a missing link between poor diet and higher cancer risk
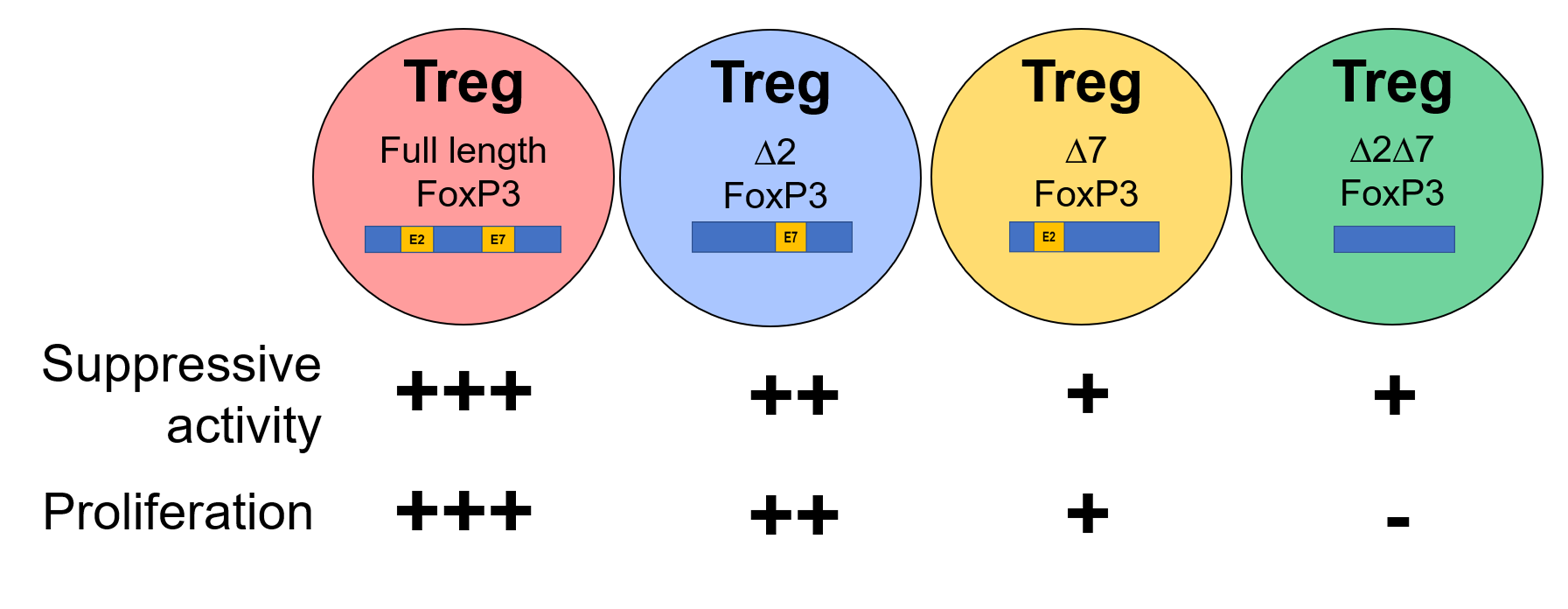
National University of Singapore (NUS)A research team from the National University of Singapore (NUS) has unearthed new findings which may help explain the connection between cancer risk and poor diet, as well as common diseases like diabetes, which arise from poor diet.