Space Oddity: Uncovering the Origin of the Universe’s Rare Radio Circles
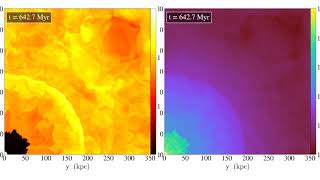
University of California San DiegoA team led by UC San Diego Professor of Astronomy and Astrophysics Alison Coil believes they may have found the origin of the universe's giant odd radio circles: they are shells formed by outflowing galactic winds, possibly from massive exploding stars known as supernovae.