AI training: A backward cat pic is still a cat pic
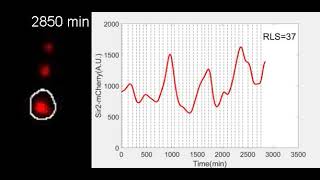
Cold Spring Harbor LaboratoryThe instructions for gene regulation are written in a complicated code, and scientists have turned to artificial intelligence to crack it. To learn the rules of DNA regulation, they’re using deep neural networks (DNNs), which excel at finding patterns in large datasets. DNNs are at the core of popular AI tools like ChatGPT.